
A control system is a system of devices or mechanisms that are designed to manage, regulate, or manipulate the behavior of other systems or processes.
The primary purpose of a control system is to ensure that the output or performance of the controlled system matches a desired reference or setpoint as closely as possible.
Control systems are widely used in engineering, automation, and various applications to achieve specific objectives.
There are 2 main types of control system:
An open loop system is a control system where the output has no effect on the controlling action of the input system.
Example – Automatic Room Heating System
A simple example of an open look system is a central heating system based on a timer. It is generally colder at night so the central heating system is programmed to turn on at 6pm and turn off a 6am.
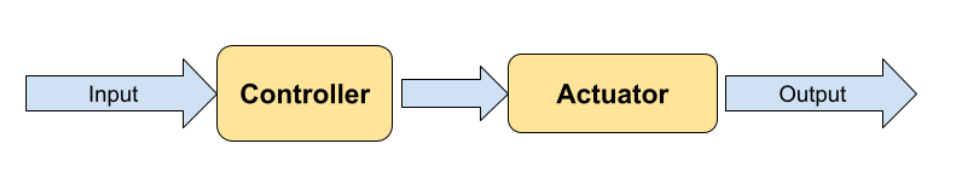
What is an open loop control system?
Which of the following is a disadvantage of open loop control systems?
A closed-loop system, also known as a feedback control system, is a type of control system in which the system's output is continuously monitored and compared to a desired or reference input value.
The system then uses this feedback information to make real-time adjustments to the control input in order to maintain the output as close as possible to the desired value. This is known as the feedback loop and is a core component of a closed loop system.
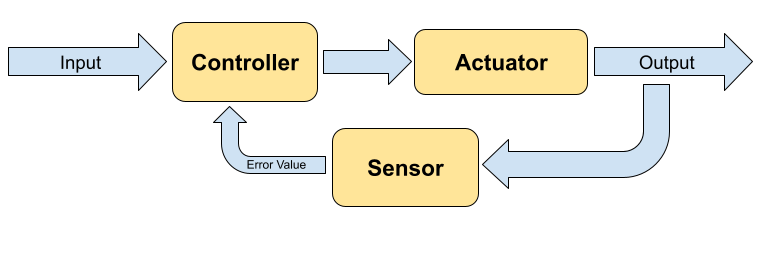
closed loop control system
What is the purpose of feedback in closed loop control systems?
Generally more accurate and response to environmental changes than open loop systems.
More complicated than open loop systems and therefore more expensive and prone to bugs.
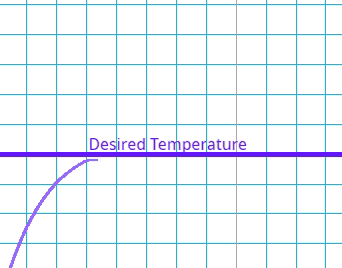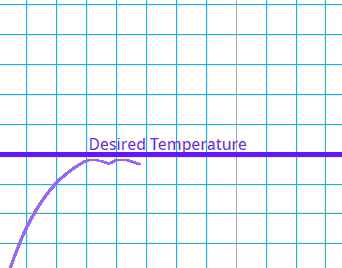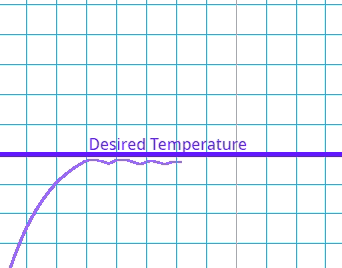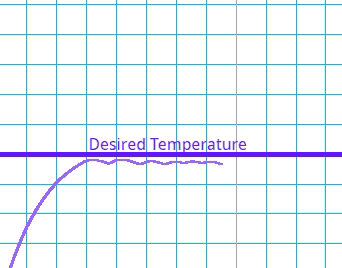
This is where the system goes past the target value and has to readjust.
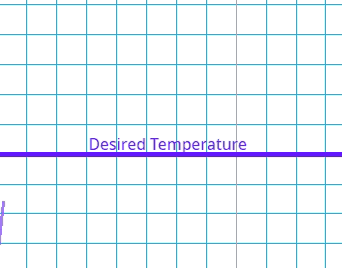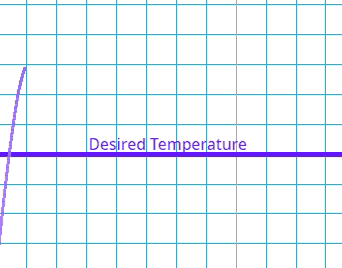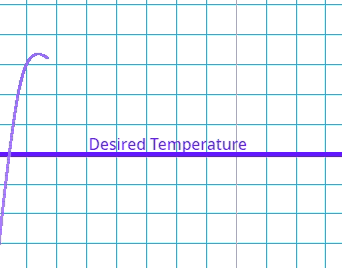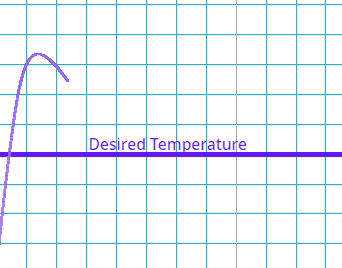
Which type of error occurs if the system's output exceeds the desired value before settling at the steady state?
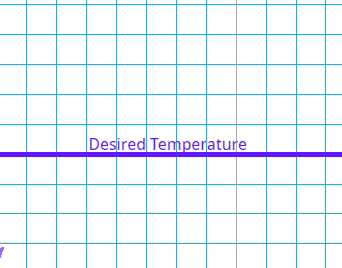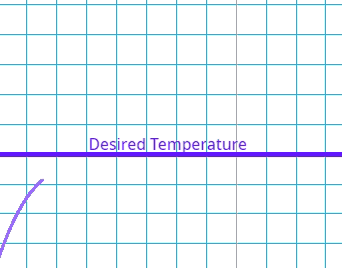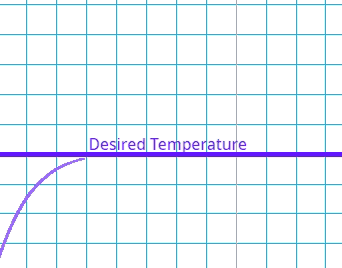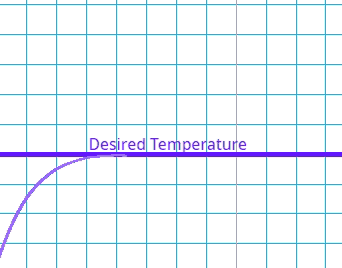
This is where there is a delay between the error being identified and the system compensating.
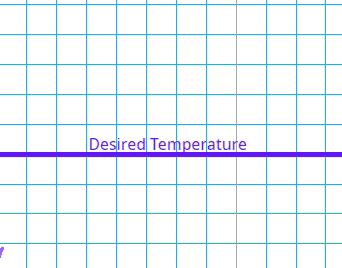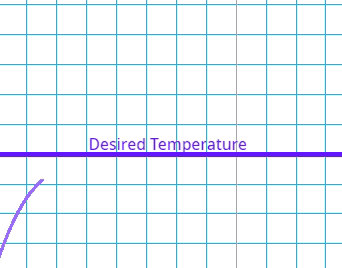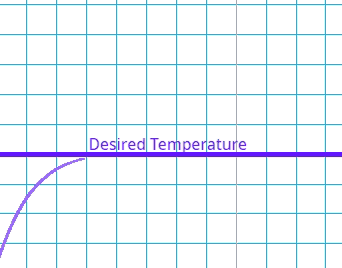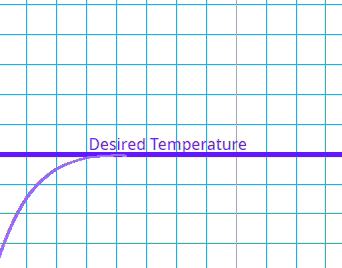
What is the effect of a high delay error in a control system?
Once the system has reached equilibrium it may have a constant error where it never reconciles with the target value.
These systems operate with signals that are continuous in both time and amplitude. In other words, the system inputs, outputs, and internal states can change smoothly over time.
These systems operate with signals that are discrete in time, meaning they work at specific intervals. Input and output signals are sampled at distinct times.
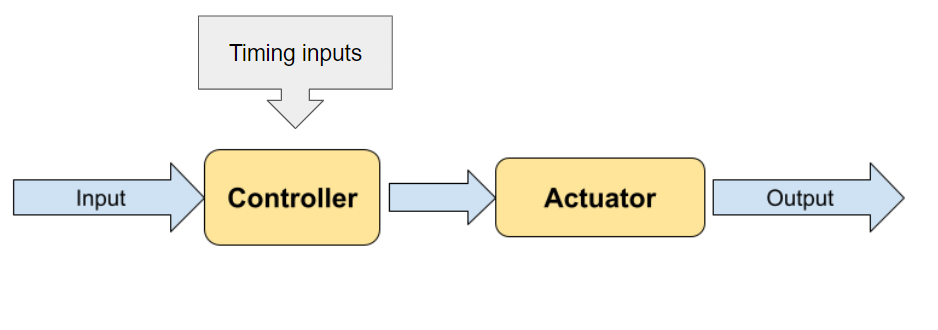
A feedforward system is a type of control system where the control action is determined by the input without considering feedback from the output.
The system anticipates the effect of disturbances and compensates for them in advance.
A simple example of a feedforward system is an automatic sprinkler system for a garden. The system is programmed to turn on the sprinklers at 6am every day for 30 minutes, regardless of the soil moisture level or weather conditions.
The system does not adjust based on feedback from the garden (e.g., how much water the plants actually need), but instead operates solely on a pre-determined schedule, assuming that water is required at that time.
When a microphone picks up sound from a speaker, it leads to a loud, uncontrolled feedback loop.
Chain reactions, such as nuclear reactions, where the output boosts the input, leading to exponential growth.
Blood clotting, where each step accelerates the next to rapidly stop bleeding.
Negative feedback occurs when the system uses an output signal to reduce or dampen the effect of a process. In other words, the feedback signal works to oppose the input.
Purpose
It stabilizes the system, helps maintain balance, and keeps outputs close to desired values.
Effect
Leads to a self-regulating process that seeks an equilibrium point and rejects disturbances.
In a heating system, if the temperature rises above a set point, the heater turns off. If it falls below, the heater turns on.
The system adjusts fuel supply to maintain a constant speed.
Human body temperature regulation (e.g., sweating when it’s hot).
Reduces errors and stabilizes systems.
Increases system accuracy and reliability.