

Dynamic microphones are rugged, durable, and designed to handle high sound pressure levels (e.g., loud environments). They use electromagnetic induction to convert sound into electrical signals.
Live Performances: Used by singers, musicians, and public speakers during live events because they can handle high volumes without distortion.
Podcasting and Streaming: Sometimes used in casual podcasting setups due to their durability and simplicity.
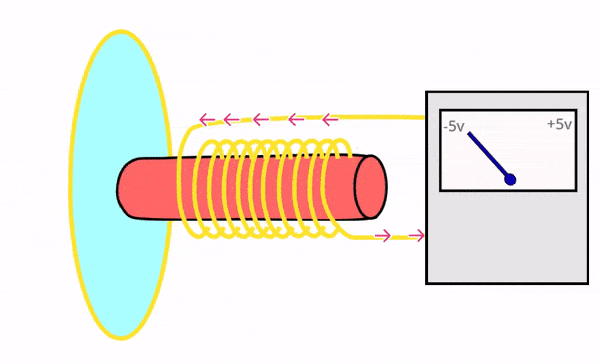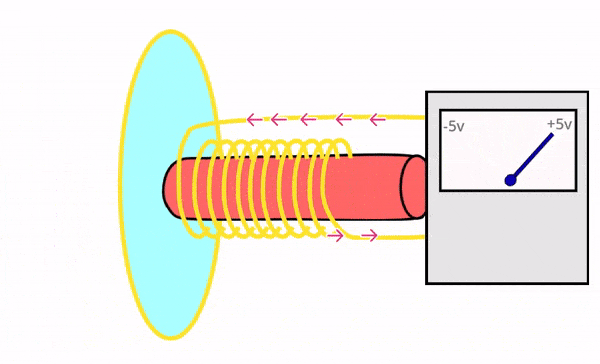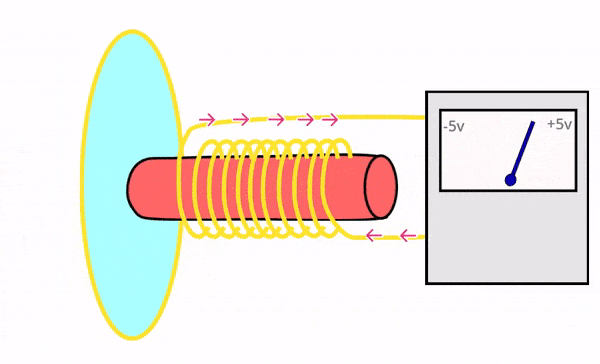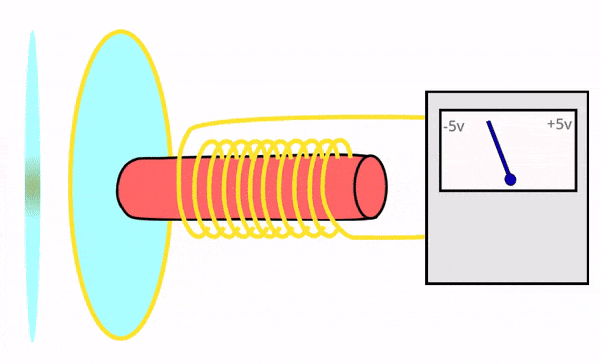
Can withstand rough handling and extreme sound levels without damage, making them ideal for live performances.
Typically less expensive than condenser microphones, making them accessible for a variety of uses.
Does not require an external power source like phantom power, simplifying the setup.
Dynamic mics are less sensitive to subtle sound details compared to condenser microphones, which can affect the quality of recordings for quieter or more delicate sound sources.
Not ideal for capturing the full range of sound frequencies, making them less suitable for studio recordings that demand detailed sound reproduction.
Condenser microphones are more sensitive and typically used in studios for capturing high-quality sound. They operate by using a diaphragm and require an external power source (phantom power).
Common Uses
Ideal for recording vocals, acoustic instruments, and podcasts where high sound quality is essential.
Often used in radio stations or podcasting studios for crystal-clear sound reproduction.
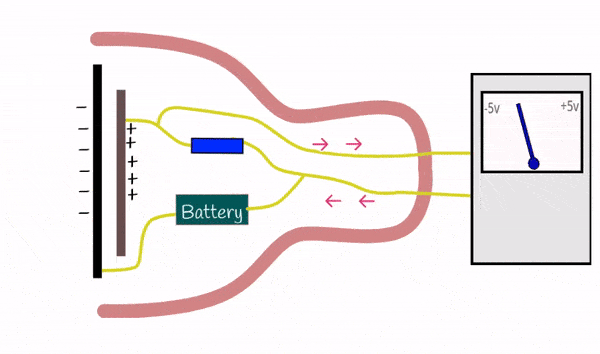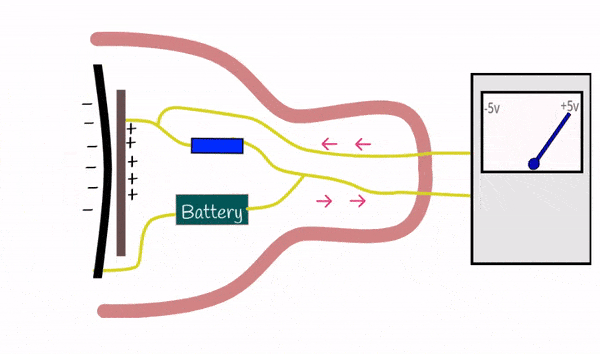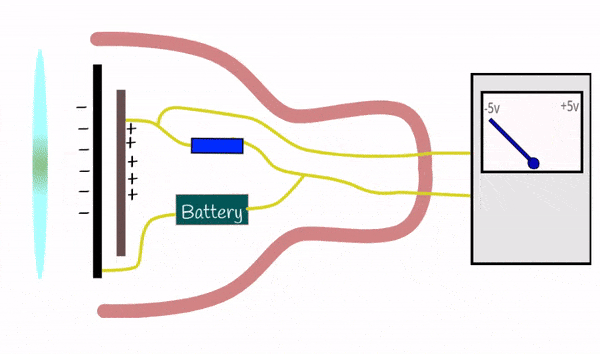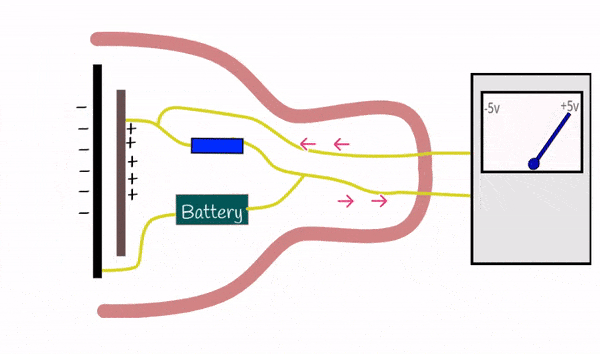
Excellent for capturing detailed and nuanced sounds, making them ideal for professional recording environments, voiceovers, and vocals.
Capable of capturing a broader range of frequencies, from low to high, which results in more accurate sound reproduction.
What is the advantage of a condenser microphone over a dynamic microphone?
They are more delicate than dynamic mics and can be easily damaged by rough handling or high sound pressure levels.
Needs phantom power, typically provided by an audio interface or mixer, which adds to the complexity of the setup.
What is phantom power used for?
A sound card is a hardware component in a computer that handles audio input and output, converting digital audio signals to analog DAC (for speakers) and analog signals from microphones to digital ADC (for recording).
While many computers have built-in sound capabilities (integrated sound chips), dedicated sound cards offer superior audio quality and more features.
Types of Sound Cards
What does a sound card do?