
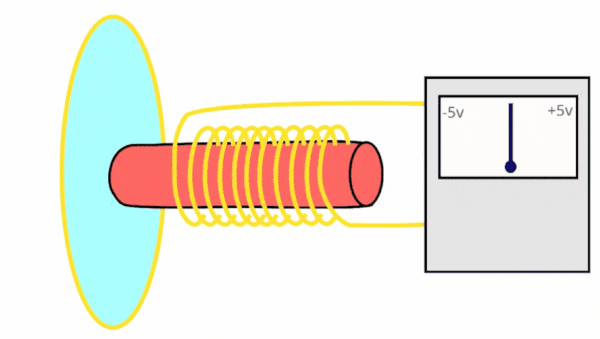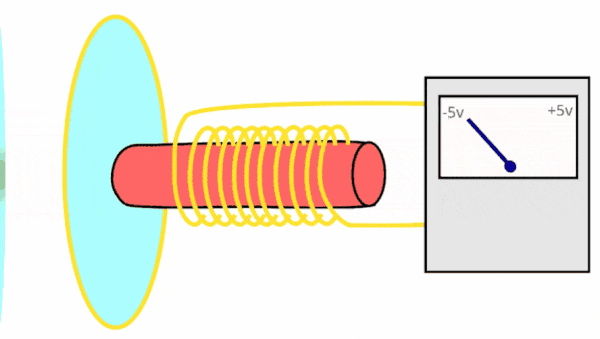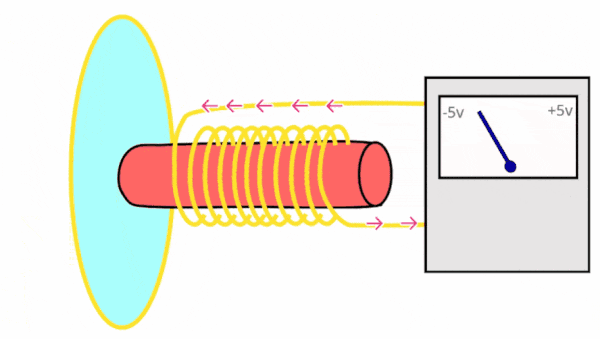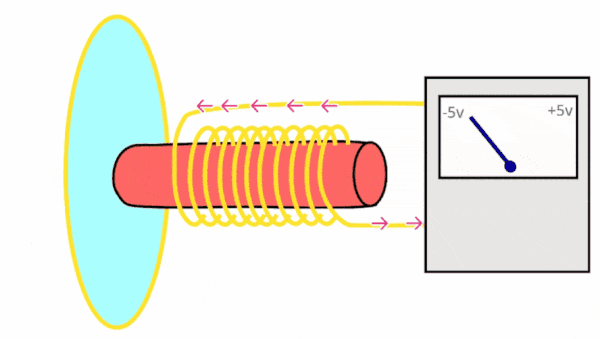
Dynamic microphones perform analogue to digital conversion (ADC) using the following process:
Durability: Dynamic microphones are robust and can handle rough handling, making them ideal for live performances.
High Sound Pressure Levels (SPL): They can handle loud sounds without distortion, making them great for miking drums, guitar amps, or live vocals.
No External Power Required: They do not need an external power source (like phantom power) to operate.
Cost-Effective: Dynamic mics tend to be more affordable than condenser microphones, especially for good quality models.
Less Sensitive to Background Noise: Because they are less sensitive than condensers, dynamic mics are better in noisy environments or for capturing louder sound sources.
Lower Sensitivity: They are not as sensitive to subtle or quiet sounds, which can be a disadvantage for recording delicate vocals or acoustic instruments.
Limited Frequency Response: While adequate for many uses, dynamic microphones typically have a more limited frequency range and may not capture high-frequency details as well as condensers.
Less Detail and Clarity: Compared to condensers, dynamic mics may produce a less clear and detailed sound, especially for studio recording.
How does a dynamic microphone work?
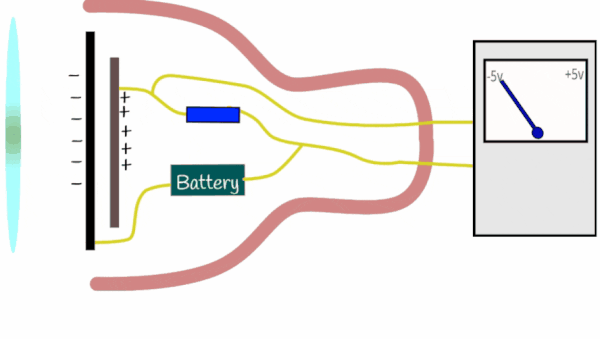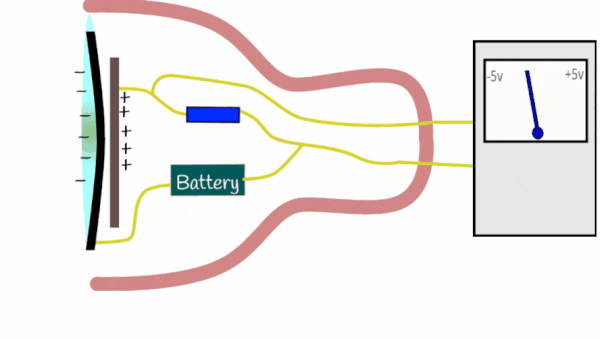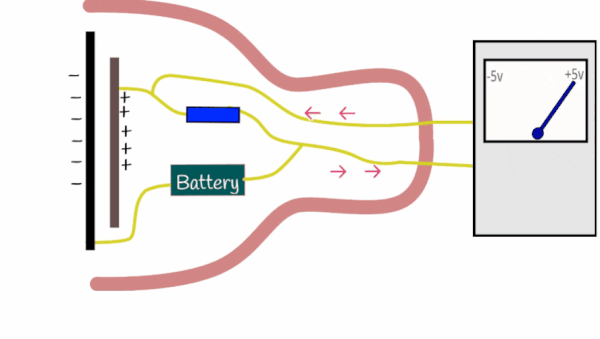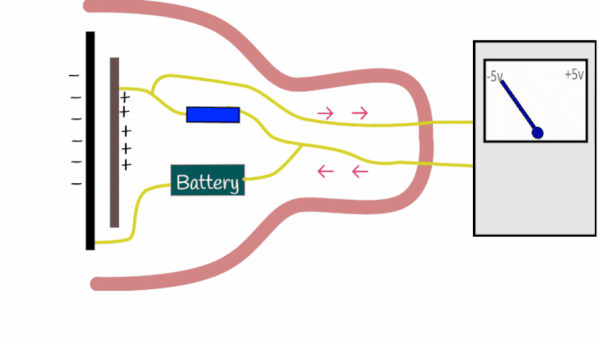
Condenser microphones perform analogue to digital conversion (ADC) using the following process:
High Sensitivity and Detail: Condenser microphones are more sensitive to sound, capturing detailed and nuanced performances, which makes them great for studio recordings, vocals, and acoustic instruments.
Wider Frequency Response: They can capture a broader range of frequencies, from very low to very high, making them ideal for recording instruments that require precision and clarity.
Better for High-Fidelity Recording: Their sensitivity and accuracy make them preferred for recording vocals, strings, and other delicate sources in a controlled studio environment.
Enhanced Clarity and Precision: Condenser mics provide a more accurate and natural sound, making them the go-to for professional-quality audio recordings.
Fragility: Condenser microphones are more delicate than dynamic ones and can be easily damaged if mishandled.
Requires Power: They need external power (usually phantom power from an audio interface or mixer) to operate, which may not always be available in live settings.
Expensive: High-quality condenser microphones tend to be more expensive than dynamic ones.
Sensitive to Background Noise: Due to their sensitivity, they can pick up unwanted ambient noise, making them less suitable for noisy environments or live performances.
Cannot Handle High SPLs Well: Condenser mics may distort when exposed to very loud sounds, so they are not ideal for miking high-SPL sources like drums or guitar amplifiers in live situations.
How does a condenser microphone generate a signal?
Which of the following is a disadvantage of condenser microphones?
Sound Representation